Original Source
“What’s a Fat-Burning Heart Rate, and How’s It Calculated?”
Engaging in exercises that elevate your heart rate to the fat-burning zone can contribute to effective fat loss. The particular heart rate suitable for this purpose may vary based on your age.
Monitoring your heart rate is a valuable tool to gauge the intensity of your workout. Typically, at rest, most individuals experience a heart rate between 60 and 100 beats per minute, according to trusted sources. As you engage in physical activity, your heart rate naturally rises, and the intensity of the exercise correlates with the extent of this increase.
When you exercise within the fat-burning heart rate zone, your body shifts its energy source from readily available sugars and carbohydrates to tapping into stored fat. This targeted approach promotes fat loss, making your workout more effective for achieving your fitness goals.
Other heart rate zones are:
- → resting heart rate
- → moderate heart rate
- → target heart rate
- → maximum heart rate
Calculating your fat-burning heart rate involves targeting approximately 70% of your maximum heart rate.
Your maximum heart rate represents the highest number of beats per minute your heart should reach during physical activity. To find this maximum, simply subtract your age from 220.
As an example, let’s consider a 35-year-old individual. Subtracting 35 from 220 gives a maximum heart rate of 185 beats per minute. To pinpoint the ideal fat-burning zone, aim for 70% of this maximum, which in this case is around 130 beats per minute. Keeping your heart rate within this range can optimize your workout for efficient fat burning.
Determining various heart rate zones is crucial for optimizing your workouts.
Experts suggest aiming for 70 to 85 percent of your maximum heart rate for vigorous activity, commonly referred to as your target heart rate. This intensity level ensures an effective workout.
On the other hand, if you’re engaging in moderate exercise, your heart rate should fall between 50 and 70 percent of your maximum heart rate. This range provides a balanced and sustainable level of effort during your workout.
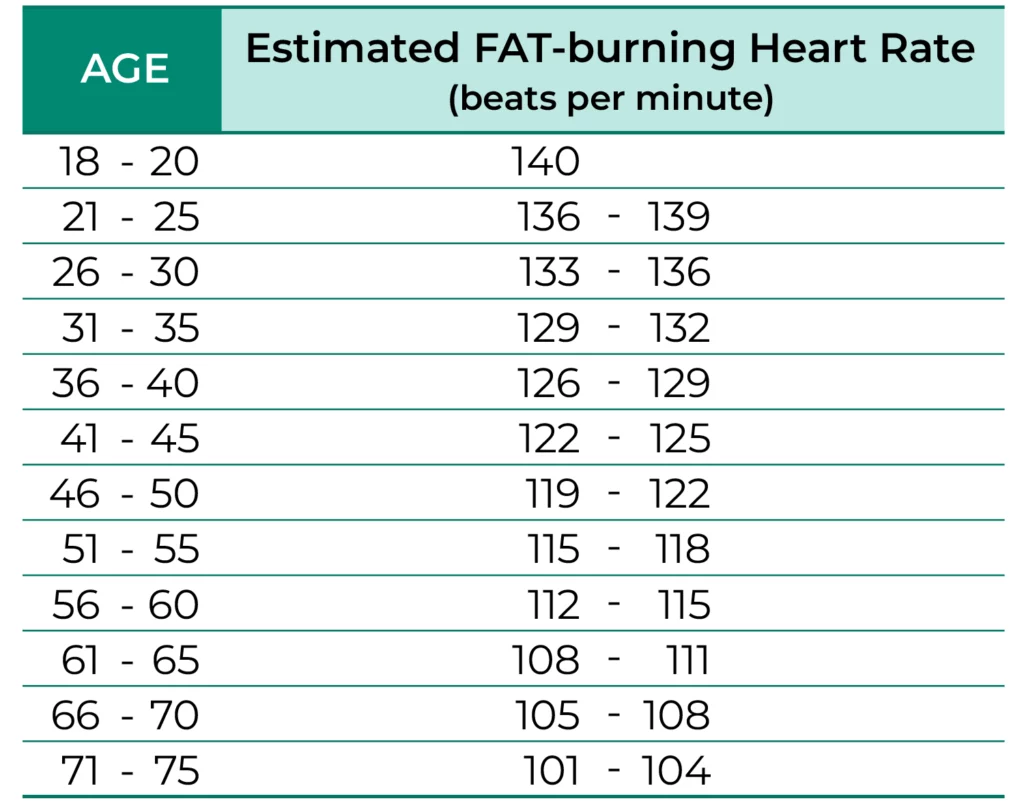
Chart for Optimal Fat-Burning Heart Rate
When referencing the provided chart, it’s important to note that fat-burning heart rates tend to decrease with age. For instance, if you’re 32 years old, consider utilizing the higher end of the 31 to 35 age range for optimal fat-burning heart rate.
Additionally, be aware that certain medications can impact your heart rate. If you have any concerns, it’s advisable to consult with your doctor.
Tools to measure Heart Rate
Various tools are available for monitoring heart rate, catering to different preferences and needs; this means you don’t necessarily need expensive equipment to get your basic heart rate. The choice is yours to make, based on personal preferences, your preferred exercise, budget, and the features of the specific device.
➡️ Traditional tracking

Utilizing traditional methods involves placing your fingers on pulse points (neck, wrist, or chest) to manually measure your heart rate. Stop exercising, count your heartbeats for 60 seconds (or 30 seconds multiplied by two), and the resulting number indicates your heart rate.
➡️ Wrist monitor
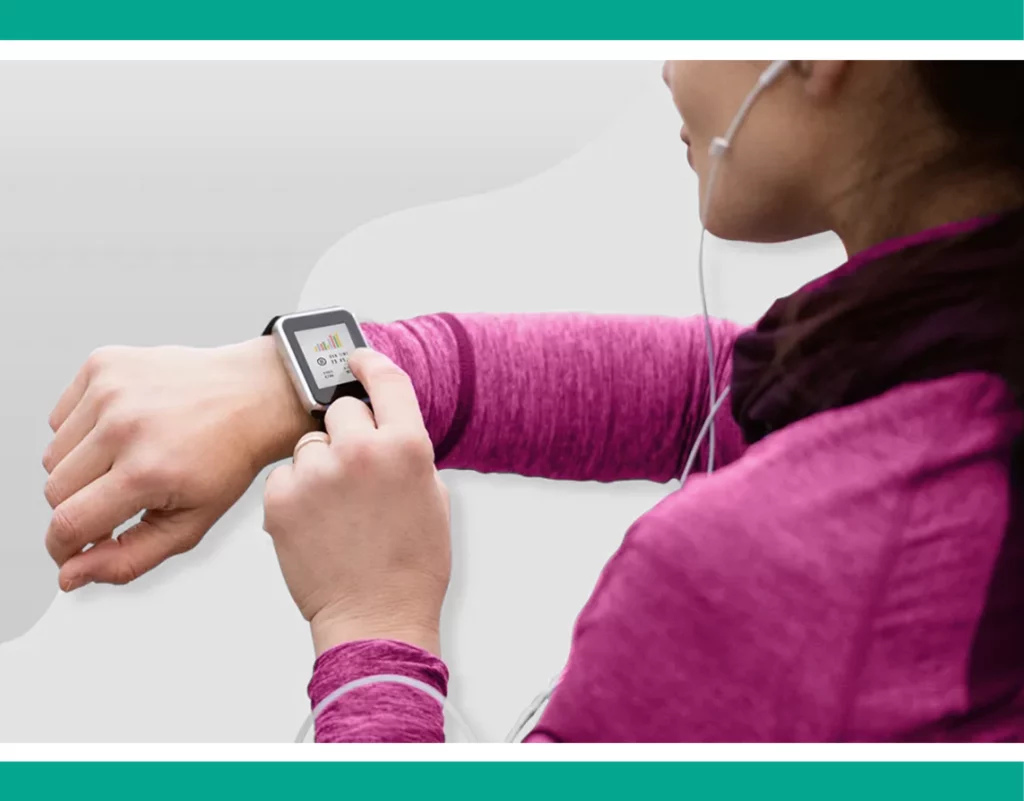

These devices have gained popularity for seamlessly attaching to the body like a conventional watch. You can continually track your pulse throughout the day, determining your activity zones (fat-burning, resting, moderate, or maximum) without interrupting your routine. Additionally, they often provide comprehensive data, including daily steps, workout distance, calorie burn, and floors climbed, while functioning as a regular timepiece.
➡️ Chest strap monitor
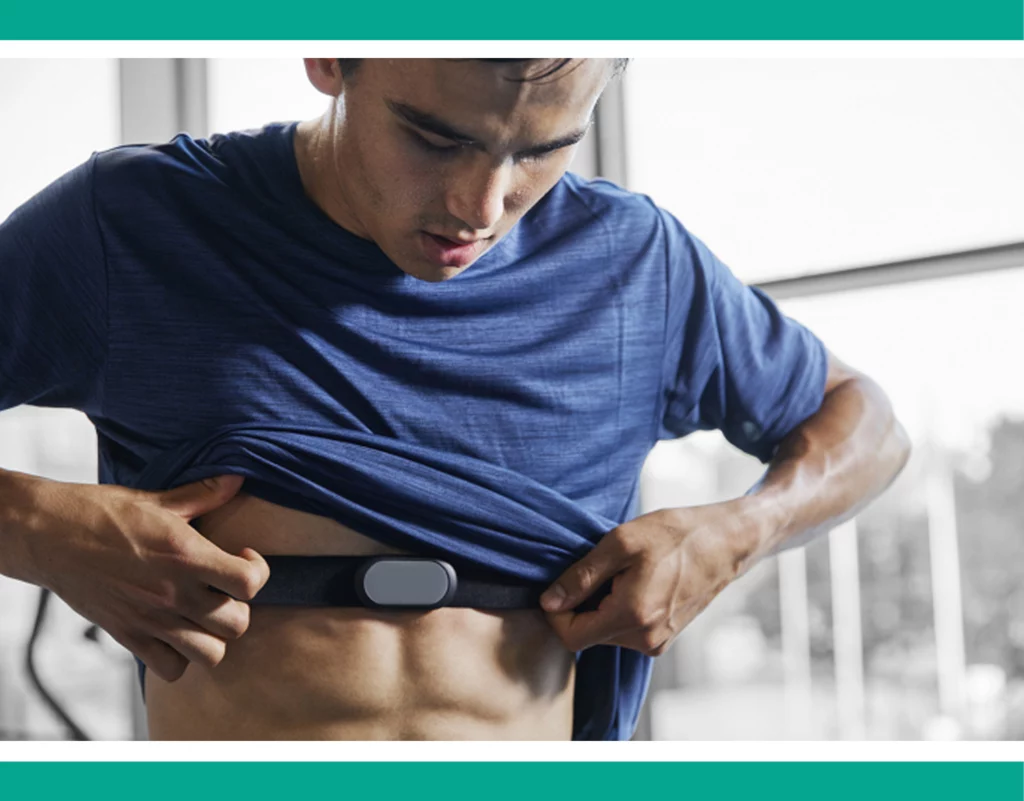

Chest strap heart rate monitors fasten around your chest, tracking your heart rate during exercise. Notably, premium options like Garmin’s Heart Rate Monitor wirelessly transmit data to your compatible device, often a watch, providing a comprehensive overview of your workout. These straps, crafted from soft, adjustable fabric, accommodate various body sizes.
Versatile in use, chest strap monitors are suitable for most activities, including swimming. However, it’s essential to carefully review all features before purchasing. While some devices are waterproof, allowing submersion, others are water-resistant, suitable only for short periods in the water.
Selecting an exercise routine
for FAT BURNING

Identifying the most effective workouts for entering the fat-burning zone is a personal endeavor, with heart rate monitoring serving as a crucial guide.
Optimal fat-burning occurs during moderate activities, as indicated by the ability to maintain a conversation without being too breathless. The talk test can help distinguish between moderate and vigorous levels. Additionally, gauging exercise intensity based on individual capacity, where fat-burning activities fall within the 11 to 14 range on a scale from 1 to 20, ensures a targeted and sustainable approach to fitness. If intensity surpasses 17 to 19, it’s advisable to scale back, as it indicates more vigorous activity.
Consider incorporating these exercises to achieve your fat-burning zone:
◾️ Slow jogging or running.
◾️ Brisk walking
◾️ Swimming
◾️ Cycling (under 10 miles per hour)
◾️ tennis
◾️ High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT)
◾️ Jump rope
◾️ Rowing
◾️ Dancing
◾️ Elliptical training
◾️ Kickboxing or martial arts workouts
Although your primary goal may be fat loss, it remains crucial to periodically elevate your heart rate into the vigorous zone. Engaging in higher-intensity exercises not only fortifies your cardiovascular system but also burns more calories compared to moderate activities.
Consider incorporating interval training into your workout routine as well. This involves alternating between walking and running in distinct intervals. Such a workout approach proves to be highly effective for fat loss while simultaneously enhancing your cardiovascular fitness.
Simple tips to achieve fat loss
In addition to physical activity, adopting other healthful habits can contribute to fat loss and a reduction in overall weight.
✔️ Prioritize a Nutrient-Rich Diet:
Emphasize whole foods, with a substantial portion of your plate dedicated to fruits and vegetables. Opt for whole grains, lean proteins, and low-fat dairy. While grocery shopping, focus on the store’s perimeter and minimize intake of added sugar and saturated fats commonly found in packaged foods.
✔️ Stay Hydrated:
Choose water over sugary beverages like juice or soda to avoid unnecessary calories. If plain water isn’t appealing, consider adding a hint of artificial sweetener or a squeeze of lemon for flavor.
✔️ Mind Your Portions:
Be mindful of portion sizes, especially when dining out. Requesting half of your meal to be packaged before you start eating can prevent overeating. At home, opt for smaller plates, such as a salad-sized plate instead of a dinner-sized one.
✔️ Strive for Gradual Weight Loss:
Aim for a slow and steady approach to weight loss, aiming for no more than two pounds per week. Consult with your doctor to establish a healthy and sustainable weight loss goal, and seek guidance from a dietitian if needed.
If you’re just starting out with physical activity, it’s important to proceed gradually. Following the American Heart Association’s advice, begin at a moderate intensity (around 50 percent of your maximum heart rate) to minimize the risk of injury and prevent burnout before progressing to higher intensities.

