Original Source
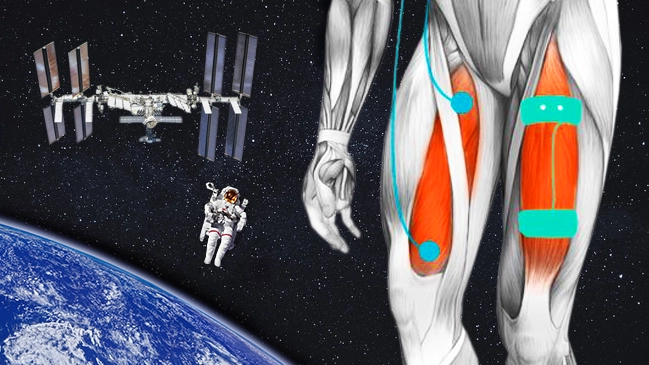
“Wired for space – Muscle stimulation to enhance astronaut health”
Space exploration poses distinctive health challenges for astronauts, arising from factors such as microgravity, isolation, and radiation exposure. The European Space Agency’s (ESA) SciSpacE initiatives are dedicated to comprehending these effects and their ramifications for human well-being during prolonged missions.
ESA collaborates closely with scientists to execute experiments in both microgravity and analogous environments, shedding light on the repercussions of space-related stressors. Among the primary concerns is the adverse impact on muscles and bones, despite astronauts adhering to daily exercise regimens. In response, ESA is investigating the potential of electrical stimulation as a countermeasure, with planned testing aboard the International Space Station.
The focal point of this research is the “Muscle Stimulation” experiment. Through the application of controlled electrical currents to leg muscles, the study aims to augment muscle mass, strength, and recovery. Complementary evaluations, encompassing MRI scans, microcirculation analyses, and blood sample assessments, will contribute to a comprehensive understanding of its effectiveness.
The benefits of addressing these challenges may extend beyond space exploration and have relevance on Earth. The knowledge acquired holds the potential to enhance healthcare for diverse populations, ranging from the elderly to clinical patients and athletes.